Services
Intra-abdominal Lymph Node Biopsies
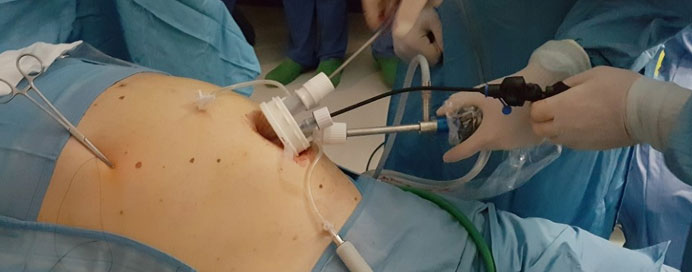
Intra-abdominal lymph node biopsies are diagnostic procedures used to obtain tissue samples from lymph nodes located within the abdominal cavity. Lymph nodes are part of the lymphatic system, which helps fight infections and filter lymph fluid containing immune cells throughout the body. Biopsies of intra-abdominal lymph nodes are typically performed to investigate abnormalities such as enlarged nodes detected on imaging studies like CT scans or PET scans. These abnormalities may indicate various conditions including lymphoma, metastatic cancer spread from other organs, or infections.
The procedure can be performed using different techniques depending on the location of the lymph nodes and the suspected underlying condition:
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
This minimally invasive technique involves inserting a thin needle through the skin into the enlarged lymph node under imaging guidance (such as ultrasound or CT scan) to withdraw small tissue samples for examination.