Services
Pancreatic Endotherapy
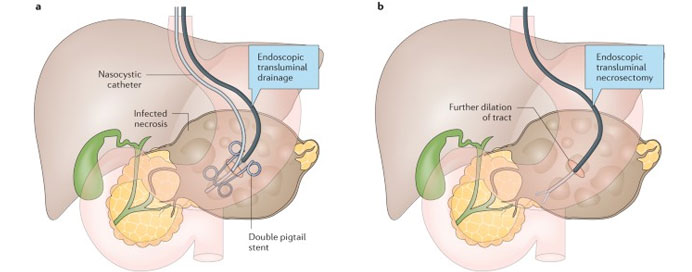
Pancreatic endotherapy refers to a range of endoscopic procedures aimed at diagnosing and treating pancreatic disorders, including pancreatitis, pancreatic duct strictures, pseudocysts, and pancreatic tumors. These procedures are typically performed using endoscopic techniques, such as Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), which allow for direct visualization and intervention within the pancreas. During pancreatic endotherapy, specialized endoscopic tools, such as stents, balloons, or lasers, may be used to treat conditions such as pancreatic duct strictures by widening the duct and restoring normal drainage. Additionally, procedures like endoscopic cyst gastrostomy can be used to drain pancreatic pseudocysts, while endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) enables the sampling of pancreatic tumors for diagnostic purposes. Pancreatic endotherapy offers several advantages, including its minimally invasive nature, reduced risk compared to surgical interventions, and shorter recovery times. However, it requires specialized expertise and equipment and carries a risk of complications such as pancreatitis or bleeding. Overall, pancreatic endotherapy plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of pancreatic disorders, providing effective treatment options and improving patient outcomes.