Services
ESD
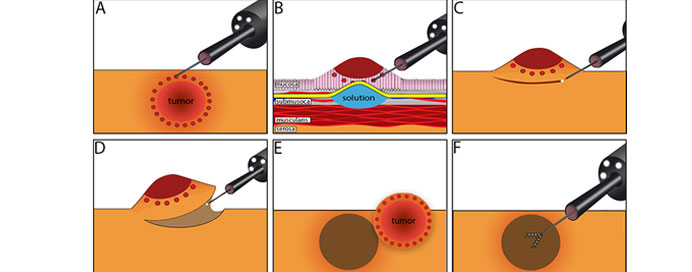
ESD stands for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection, a minimally invasive technique used in gastroenterology to remove large or difficult-to-reach lesions, typically found in the digestive tract. During ESD, an endoscope equipped with specialized tools is inserted through the mouth or anus to reach the lesion. Using these tools, the submucosal layer beneath the lesion is dissected, allowing for precise and complete removal of the abnormal tissue. ESD is particularly useful for treating early-stage cancers, large polyps, or lesions with unclear borders. Compared to traditional surgical methods, ESD offers advantages such as reduced invasiveness, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times. However, ESD requires advanced endoscopic skills and carries a risk of complications such as bleeding or perforation. Overall, ESD plays a crucial role in the management of gastrointestinal neoplasms, allowing for complete resection of lesions while minimizing the need for surgery.