Services
Gastro-Duodenostomy
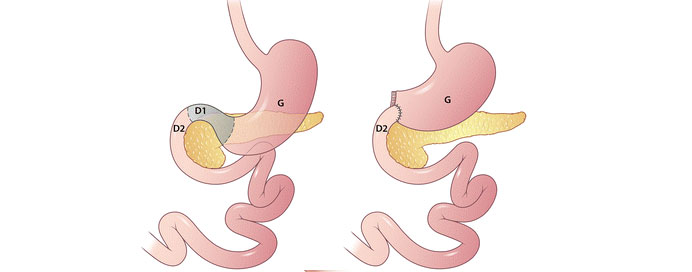
Gastro-duodenostomy is a surgical procedure involving the creation of an anastomosis (connection) between the stomach (gastro) and the duodenum (duodenostomy). This procedure is typically performed to bypass obstructions or strictures in the upper gastrointestinal tract, allowing for the passage of food and digestive fluids. Gastro-duodenostomy may be indicated in conditions such as gastric outlet obstruction, peptic ulcers, or certain types of tumors affecting the pyloric region of the stomach or the first part of the duodenum. By creating a direct connection between the stomach and the duodenum, gastro-duodenostomy aims to restore the normal flow of food and digestive juices, thereby relieving symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. The procedure can be performed using open surgical techniques or minimally invasive approaches such as laparoscopy, depending on the patient's condition and surgical preferences. Gastro-duodenostomy carries risks such as infection, leakage, or postoperative complications, and careful patient selection and surgical expertise are crucial for optimal outcomes. Overall, gastro-duodenostomy is a valuable surgical option for improving gastrointestinal function and quality of life in patients with upper digestive tract obstructions.